Recently updated on November 27th, 2025
The most effective training programs don’t rely on a single delivery method.
They incorporate a mix of interactive techniques to engage learners, build knowledge, and develop skills in a dynamic and practical way.
From scenario-based exercises to virtual reality simulations, interactive training helps participants actively participate in the learning process rather than passively observing.
In this guide, we’ll explore some of the best interactive training examples to give you some inspiration,
Let’s dive in 👇.
1. Interactive Videos
Interactive videos are designed to be used in training environments to improve engagement. They typically include clickable graphics and elements that can be used to test a learner’s knowledge of a specific topic, a classic example would be a ‘spot the hazard’ test which is a common part of many driving tests.
Unlike traditional videos, interactive videos often include:
- Multiple-choice questions that often lead to different scenarios
- Clickable links to other learning resources such as a recommended web page.
- Quizzes and polls at certain check points
Common scenarios where interactive videos are used include:
Corporate Training and Compliance: Interactive videos are used for onboarding new employees, teaching company policies, or ensuring compliance with safety regulations through engaging and scenario-based learning.
Education and E-Learning: Teachers and educational platforms use interactive videos to enhance student engagement with features like quizzes, polls, and branching scenarios.
Driving Tests and Road Safety Training: Interactive videos like ‘spot the hazard’ tests are used to assess learners’ knowledge of road safety and hazard perception.
Customer Service Training: Simulated interactions with customers help train employees to handle various scenarios effectively.
Sales and Product Demonstrations: Businesses use interactive videos to showcase products and services, allowing viewers to explore features or select use cases tailored to their needs.
Healthcare Training: Medical and healthcare professionals use interactive videos for procedural training, patient communication techniques, and simulations.
An Example of an Interactive Video
“A Date with Markiplier” is a great example of a fun interactive video experience. Created by popular YouTuber Markiplier, this project immerses viewers in a virtual date where they directly influence the unfolding narrative.
The video begins with Markiplier welcoming the viewer and taking them to a restaurant for dinner. From there, the audience is prompted to make choices, such as deciding between “Steak” or “Fish,” each leading to unique outcomes.
The storyline branches into diverse scenarios, ranging from comedic and lighthearted moments to unexpected action and suspense. The video allows viewers to explore multiple storylines and endings by rewatching and selecting different options.
2. Game-Based Learning
Game-based learning integrates gaming elements into educational environments to improve engagement and understanding. Games often include features like challenges, points, leaderboards, and interactive problem-solving scenarios, making them ideal for learners of all ages.
Unlike traditional learning methods, game-based learning often includes:
- Quests or missions that align with educational goals.
- Progress tracking through levels or points, providing instant feedback on performance.
- Collaboration opportunities, allowing learners to work together in team-based scenarios.
- Adaptive challenges that scale based on the learner’s performance.
An Example of Game-Based Learning
A somewhat surprising example of successful game-based learning is Minecraft: Education Edition, where students explore concepts in mathematics, science, and coding through engaging gameplay.
There’s even a whole body of research into the educational benefits of Minecraft, which you can in this whitepaper – highlights include:
- A study by Nolan and McBride (2014) found that using Minecraft in primary schools reduced absenteeism by 25% and increased average attendance rates by 6%.
- Another study in secondary schools reported an 18% increase in attendance and a 20% decrease in dropout rates (Romero et al., 2017).

3. Virtual Reality (VR) Training
Virtual reality (VR) training uses immersive simulations to replicate real-world environments, allowing learners to practice skills in a controlled, risk-free setting.
Unlike traditional training methods, VR training often includes:
- Fully immersive environments that replicate real-world scenarios.
- Interactive tasks requiring the learner to perform specific actions.
- Immediate feedback based on performance within the virtual environment.
Common scenarios where VR training is used include:
Military and Defense Training: VR is used to simulate combat scenarios, navigation exercises, and strategic operations, providing soldiers with realistic training experiences.
Safety and Emergency Preparedness: VR simulations help employees practice responding to emergencies, such as fires, chemical spills, or machinery malfunctions, without real-world risks.
Technical and Machinery Training: Manufacturing and construction companies use VR to teach workers how to operate complex equipment and machinery safely and effectively.
Healthcare and Medical Training: VR enables medical professionals to practice surgical procedures, diagnose patients, or learn new medical technologies in a realistic and interactive setting.
Aviation and Pilot Training: Airlines use VR flight simulators to train pilots, allowing them to experience various weather conditions, system failures, and emergency situations.
An Example of VR Training
A notable example is Walmart’s adoption of VR for employee training. The retail giant utilizes VR simulations to prepare employees for various scenarios, including customer service, compliance, and new technology implementations.
UPS, as well, uses virtual reality to train drivers on areas such as stacking packages, and handling potentially dangerous scenarios such as handling a dog attack when carrying out a delivery.
You can read more about these examples in this great article from the Wall Street Journal which explores how large companies are utilizing VR in their employee training programs.
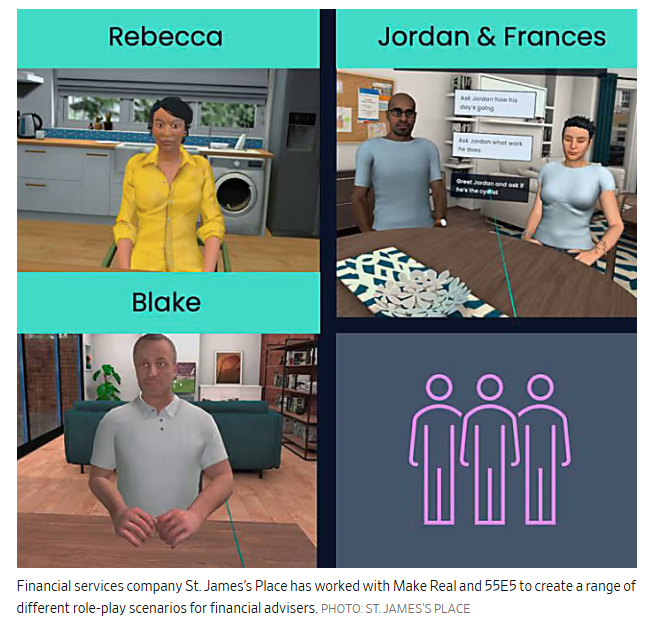

4. Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) training adds digital information to the physical world, helping learners interact with virtual elements in real-time. It is widely used to simplify complex tasks, provide hands-on practice, and improve understanding in practical settings.
For example, AR maintenance training allows workers to see virtual guides directly over machinery parts, showing how to assemble or repair components.
Common applications include:
Manufacturing and Maintenance: AR helps workers visualize complex machinery, troubleshoot issues, and learn maintenance procedures with guided overlays.
Healthcare: AR is used for medical training, such as anatomy visualization and procedural guidance, helping trainees understand complex structures and techniques.
Retail and Customer Service: AR applications assist employees in learning about products by visualizing details, assembly processes, or sales pitches.
An Example of AR Training
Boeing uses augmented reality (AR) training to improve the process of installing electrical wiring in aircraft, a task that requires absolute precision.
Technicians are equipped with Microsoft HoloLens headsets, which display real-time, hands-free, 3D wiring diagrams directly in their field of view.
This eliminates the need for traditional 20-foot-long paper diagrams, providing an intuitive and interactive guide for installing wiring harnesses throughout the aircraft.
The use of AR has increased the speed and accuracy of wiring tasks by 30%, according to Boeing, resulting in significant cost savings of millions per aircraft.
5. Scenario-Based Training
Scenario-based training places learners in realistic, job-related situations to build skills such as decision-making, conflict resolution, and customer service.
The approach allows participants to practice handling real-world challenges in a controlled environment, improving their ability to perform effectively in similar circumstances on the job.
Scenario based training includes:
- Realistic simulations that present learners with authentic workplace scenarios.
- Active decision-making that encourages learners to make choices and experience the outcomes.
- Feedback and reflection to provide detailed feedback to reinforce learning and refine skills.
Common Applications of Scenario-Based Training:
Safety Training: Workers navigate hazardous situations to develop safe practices and emergency response skills.
Corporate Training: Employees practice resolving workplace conflicts or improving negotiation skills through virtual or role-play scenarios.
Customer Service: Staff learn to manage customer complaints or complex interactions effectively.
Healthcare: Medical professionals rehearse patient communication or emergency procedures in lifelike simulations.
An Example of Scenario-Based Training
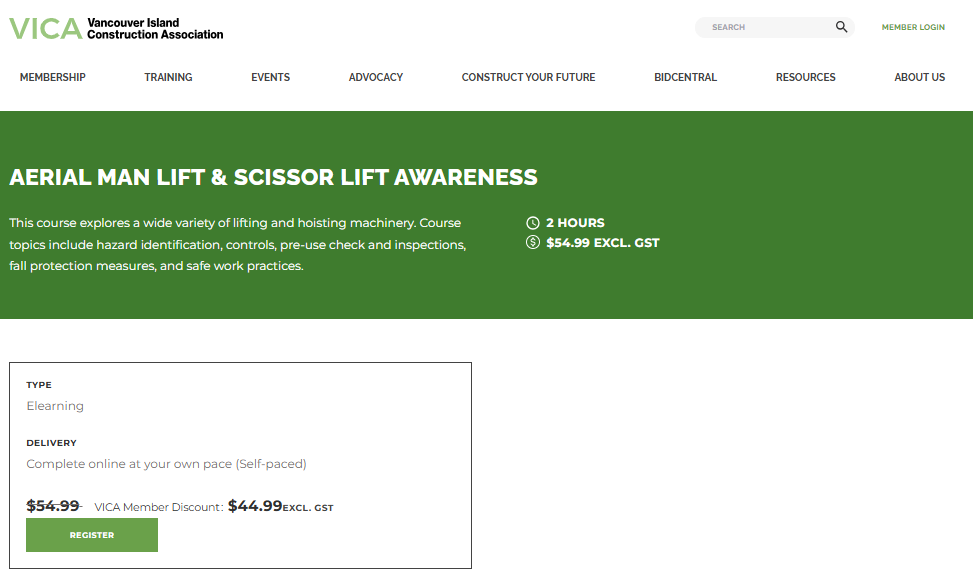
This example is from Arlo customer, the Vancouver Island Construction Association, which offers industry-leading in person and online training to 450+ members working in the industrial, commercial, institutional, and multi-family residential construction sectors on Vancouver Island, the Gulf Islands, and other coastal communities.
The Aerial Man Lift & Scissor Lift Awareness course they offer incorporates scenario-based training to prepare learners for real-world safety challenges in operating lifting and hoisting machinery.
Through the course, participants engage with practical scenarios, allowing them to apply knowledge in realistic situations, such as identifying hazards, conducting inspections, and implementing fall protection measures.
6. Interactive Presentations
Interactive presentations use tools like videos, animations, and quizzes to create a more engaging learning experience. Instead of passively watching or listening, learners interact with the material, which can make it easier to stay focused and absorb the information.
For example, a poll might let participants share their opinions on a topic, or a quiz could test their understanding in real time.
Interactive presentations often include:
- Multimedia Elements such as videos, infographics, and animations to clarify concepts.
- Live polls and quizzes to get real-time feedback and gauge audience understanding.
- Engaging content such as clickable links or branching scenarios for interactive exploration.
An Example of an Interactive Presentation
The example we’ll use for an interactive presentation comes from Arlo’s very own eLearning authoring capabilities. Inside Arlo, you can create an interactive presentation inside an eLearning course in seconds.
Simply choose to create a slideshow from the sidebar, and you’ll be able to create your slides. You can then make them as interactive as you like through elements such as checklists, flashcards, videos, and more.

7. Self-Paced Courses
Self-paced courses are the most common form of eLearning, they provide learners with the freedom to access and complete training materials on their own schedule.
Individuals can progress through the content at a pace that aligns with their unique learning preferences, which makes this format particularly suitable for those managing busy lives or differing levels of experience.
Removing the constraints of fixed timelines creates a convenient and stress-free learning environment that supports skill development on terms that work for each participant.
Key Features of Self-Paced Courses include:
- Multi-device access – self-paced eLearning Materials are designed to be accessible across devices, including computers, tablets, and smartphones, enabling learners to study from virtually anywhere
- Flexible scheduling – learners can choose when and where to engage with course materials, integrating training seamlessly into their daily routines.
- Modular structure – content is often divided into smaller sections or modules, simplifying complex topics and allowing learners to focus on one subject at a time.
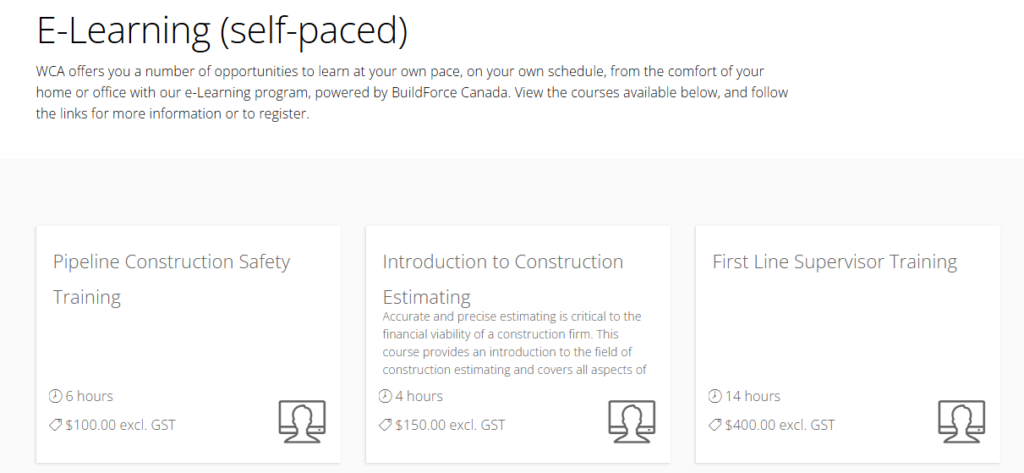
An Example of a Self-Paced Course
There are endless examples of self-paced courses. The image below shows Arlo customer, the Winnipeg Construction Association, and how they display their self-paced eLearning courses.
Again, it’s worth noting that you’ll soon be able to create self-paced courses within Arlo.
You’ll have three ways of doing this:
1. Document to Course – Upload and convert existing documents into interactive courses.
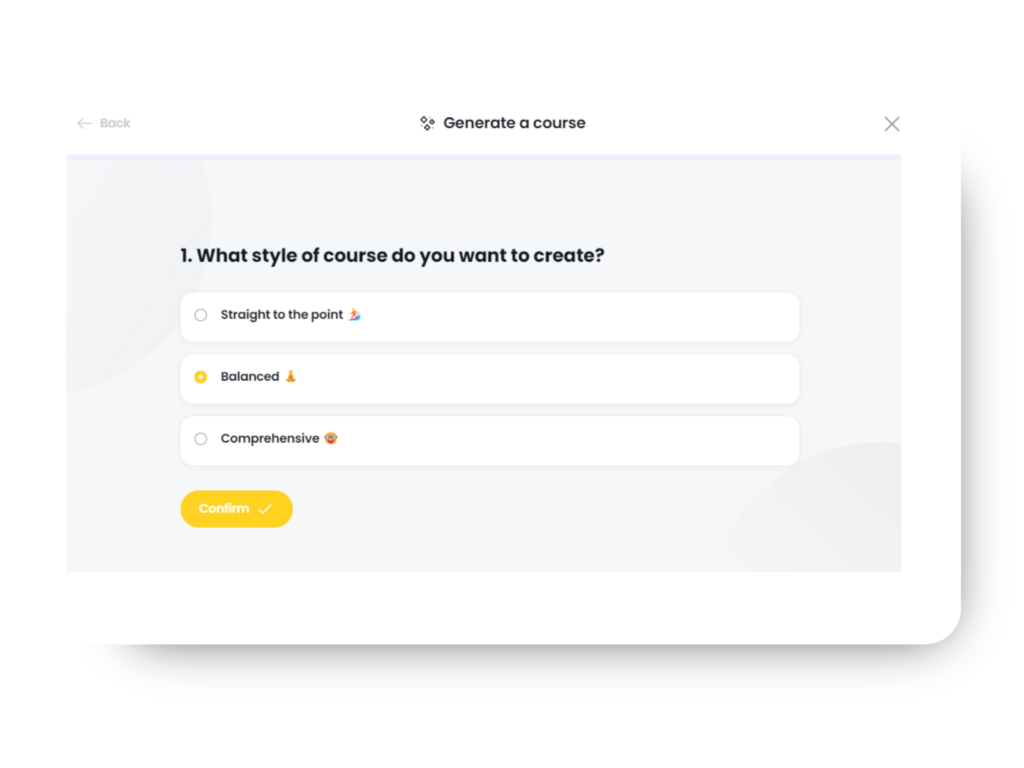
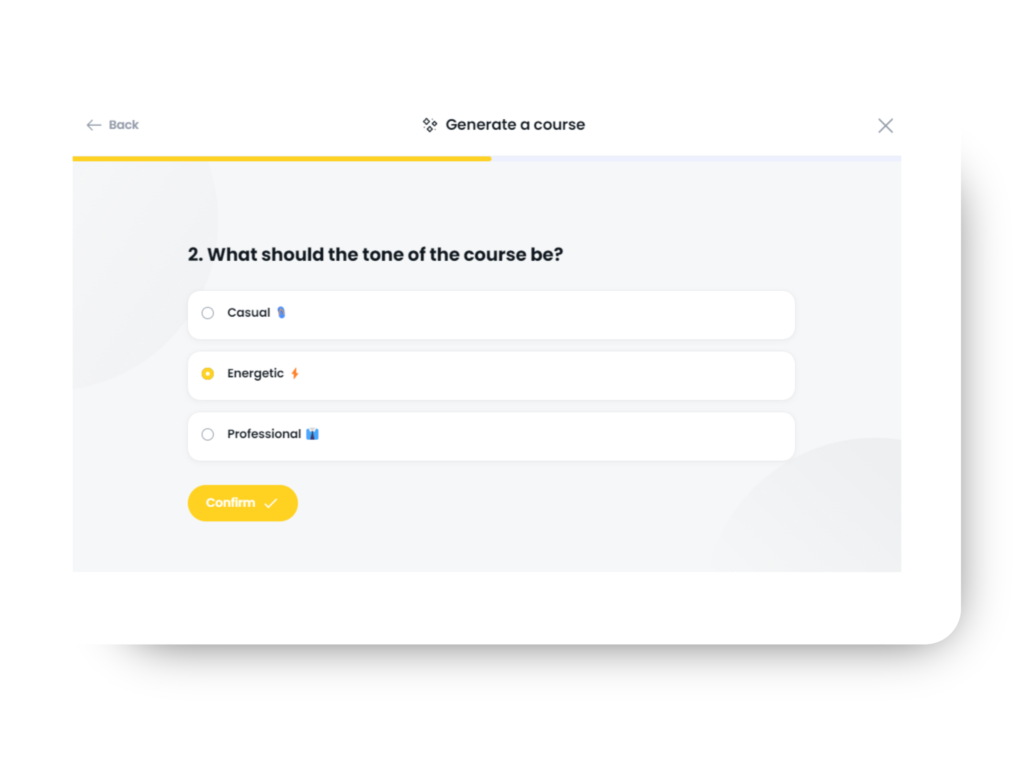
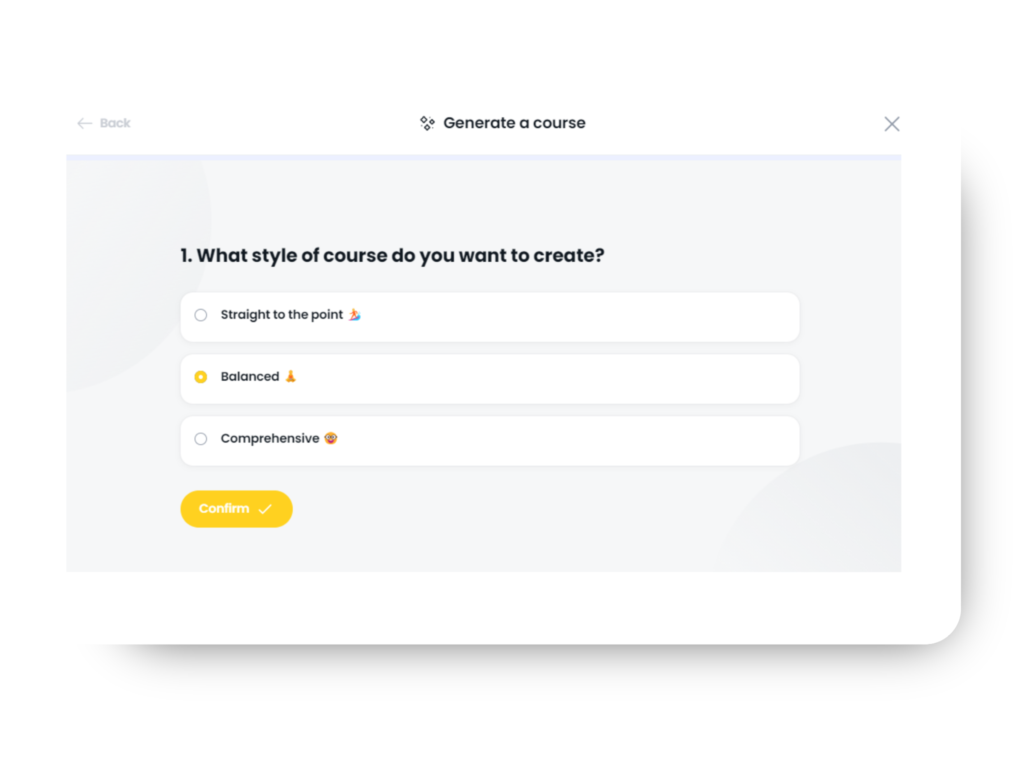
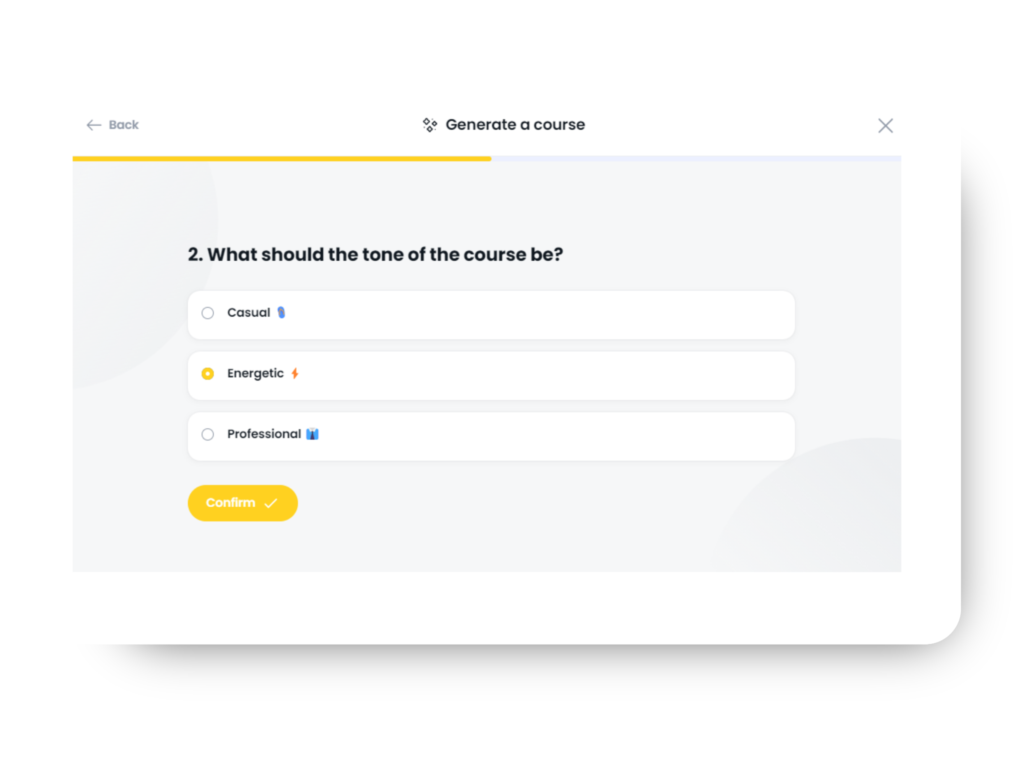
2. Generate a Course – Enter a description of your course into Arlo’s AI assistant, select your tone, style, fonts, colors, and branding, and watch as your course is created before your eyes.
3. Build Your Course from Scratch – Use Arlo’s course and quiz templates to create your course from the ground up.
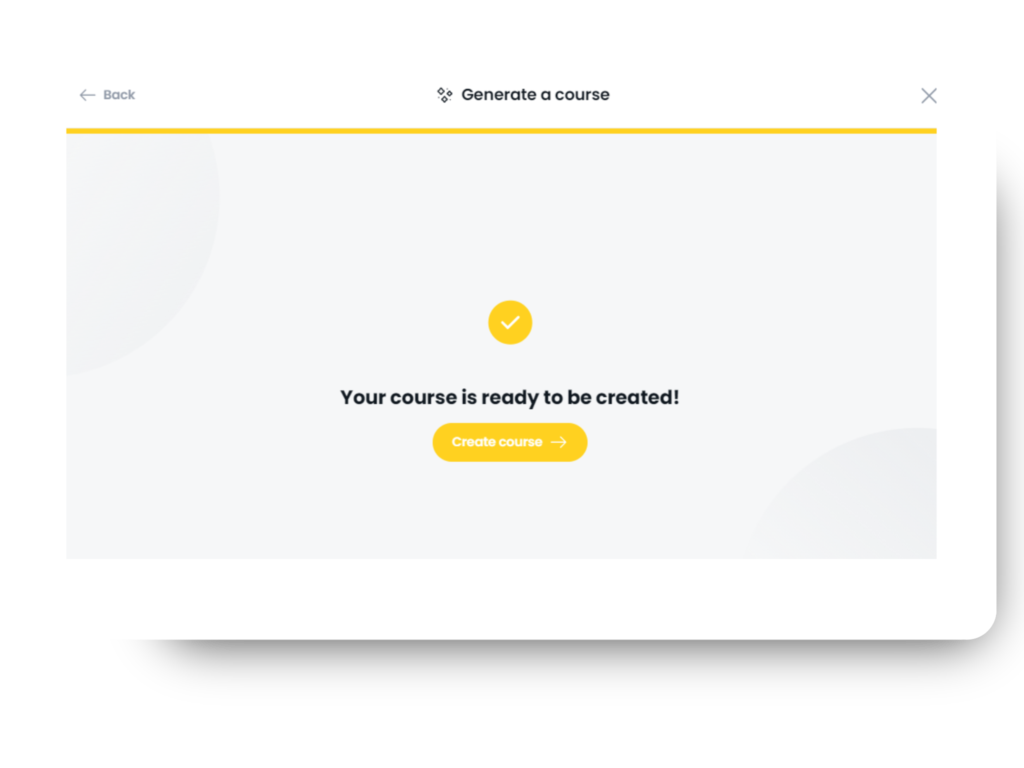
Once you’ve chosen your course creation method, you can edit the style and tone. Then, just hit “Create Course,” and your course will be created in moments, ready for you to edit.
See an example of the workflow in the images below 👇

8. Group Collaboration Exercises
Group collaboration exercises are designed to develop teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills by having participants work together on tasks or challenges.
Instead of passive learning, these exercises require active engagement. For example, teams may be tasked with planning a project under a tight deadline or managing a simulated crisis that demands quick thinking and coordination.
The structured nature of these activities allows facilitators to observe and provide feedback on how participants interact, communicate, and resolve conflicts.
Common applications include:
Corporate Training: Teams practice skills like project management, brainstorming, and conflict resolution.
Workplace Onboarding: New employees work together on simulated tasks to familiarize themselves with team workflows.
Leadership Development: Leaders participate in collaborative challenges to refine their team management skills.
An Example of Group Collaboration Exercises
For this example, were going to layout a couple of different games you can play with a team to improve their collaboration and problem solving skills.
The games are:
Bridge Build
The goal of Bridge Build is for teams to construct a sturdy bridge using limited materials within a set time frame.
How to Play:
- Divide participants into teams.
- Provide each team with building materials, such as cardboard, twine, and glue.
- Set a timer for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Teams must work together to build a bridge that can support weight.
- Judges test the bridges by placing small objects on them to determine their strength.
- If multiple bridges withstand the test, heavier objects are added until only one bridge remains standing.
Minefield
Minefield is a communication-based team-building game that challenges players to overcome obstacles and work together to achieve a shared goal. The aim is for pairs to navigate a maze without stepping on any “mines.”
How to Play:
- Set up an obstacle course with “mines,” such as traffic cones or other markers.
- Divide participants into pairs.
- Blindfold one member of each pair.
- The non-blindfolded teammate provides verbal instructions to guide their partner through the maze, avoiding the mines.
- If the blindfolded player touches a cone, the pair must start over from the beginning.
- The team that completes the course in the shortest time wins.
Related Article: 12 Virtual Training Activities and Ideas to Liven up Your Virtual Training
9. Interactive Quizzes
Interactive quizzes are structured tools designed to actively involve users in knowledge testing, decision-making, or skills assessment.
They are often enhanced with multimedia, adaptive logic, and contextual scenarios, making them ideal for practical applications and tailored feedback.
Common types of training they are used in include:
Safety and Compliance Training: Quizzes simulate workplace scenarios, such as identifying safety violations in a factory setting or selecting appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for a task.
Customer Service Training: Interactive quizzes present simulated customer interactions, testing employees on how to handle complaints, upsell products, or respond to challenging scenarios effectively.
Healthcare Training: Quizzes assess critical thinking in medical contexts, such as diagnosing patient symptoms or prioritizing care in emergency situations.
Sales Training: Trainees are quizzed on product features, objection-handling techniques, and crafting persuasive pitches using real-world sales scenarios.
Technology and Software Skills Training: Quizzes involve hands-on tasks like troubleshooting software errors, navigating user interfaces, or configuring system settings in simulated environments.
An Example of an Interactive Quiz
This example isn’t exclusively one of an interactive quiz, but it does show the positive impact quizzes can have on learner performance, in this context in a university setting.
Inspired by a faculty meeting discussion, Iowa State psychology professor Marcus Crede, along with graduate student Lukas Sotola, investigated whether frequent low-stakes quizzes could improve student outcomes.
They conducted a meta-analysis of data from 52 classes involving nearly 8,000 college students. Their findings revealed that students who took at least one quiz per week outperformed their peers on midterm and final exams and were less likely to fail.
While the studies were not randomized experiments, the evidence strongly indicates that regular quizzing, particularly when combined with immediate instructor feedback, can substantially enhance academic performance.
How Arlo Can Help You Create Interactive Training at Scale
If you’re searching for training management software help you create the interactive training types covered in this guide, Arlo is the solution.
As mentioned earlier, Arlo’s eLearning authoring features will enable you to design interactive eLearning experiences in three distinct ways.
Here’s a detailed look at how each works:
Document to Course
Step 1: Find Your Document
Arlo supports a wide range of file formats, including Word documents, PowerPoint presentations, and PDFs. If your content is stored on an external platform, simply export it as a PDF, and you’re ready to get started!
Step 2: Upload Your Document and Select Your Course Style
Upload your file to Arlo and choose the style that best suits your needs. Whether you want to focus on key information, keep it concise, or add creative flair, you have full control over the tone and design of your course.
Step 3: Watch as Your Course Comes to Life
Sit back as Arlo transforms your document into a fully interactive course. Once it’s ready, you can review it, tweak layouts, make adjustments, or dive right in and start adding more content.
Step 4: Create a Quiz
Test your learners’ understanding by generating a quiz based on your course content with just one click. Arlo makes it quick and easy to create assessments that reinforce key learning points.

Generate a Course with AI
Step 1: Provide Input to Arlo’s AI Assistant
Tell Arlo’s AI assistant exactly what you want your course to cover. The more details you provide, the better and more tailored your course will be.
Step 2: Choose Your Style, Tone, and Theme
Configure your course by selecting from a variety of styles, tones, and themes that match your needs. Finish it off with one of Arlo’s beautifully designed course themes.
Step 3: Watch Your Course Come to Life
See your course take shape as Arlo builds it section by section. Review the content as it is created and make edits or adjustments directly on the go.
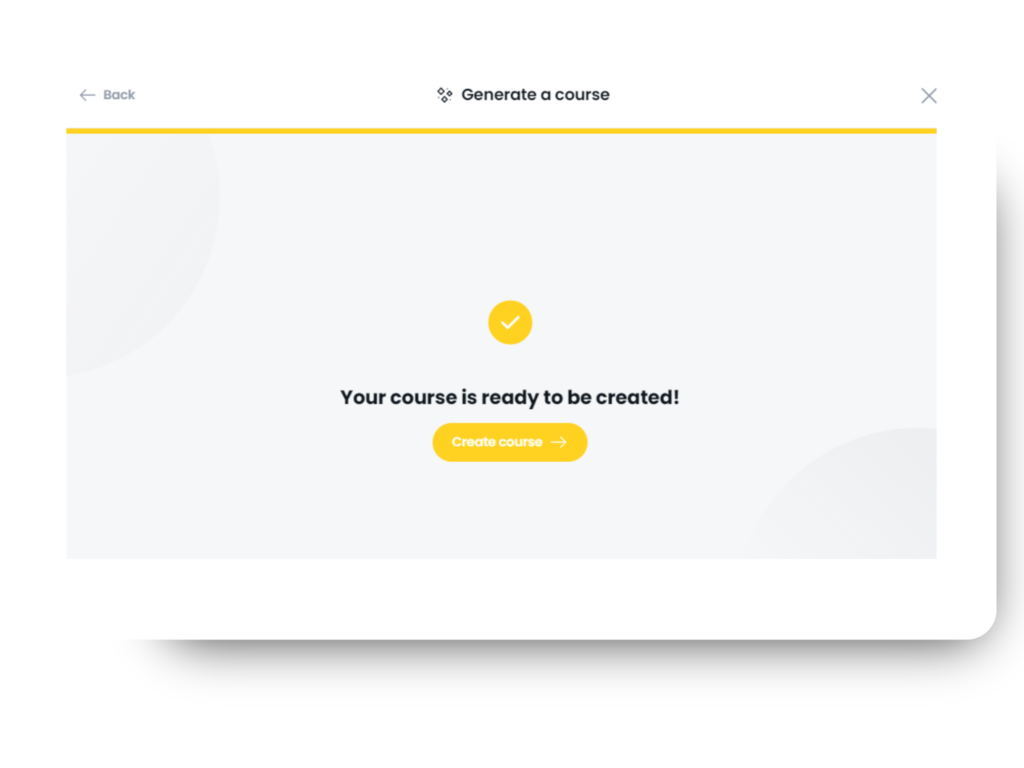
Step 4: Add a Quiz to Test Learner Knowledge
Test your learners’ understanding by generating a quiz based on the content of your course. Arlo makes it quick and effortless to add assessments and measure learner outcomes.
Build Your Course from Scratch
Step 1: Design and Structure Your Course
Use Arlo’s intuitive course interface to design interactive and visually appealing courses without requiring any technical skills. Easily structure your content, add multimedia elements, and create engaging assessments such as flashcard challenges, quizzes, training videos, or how-to guides.
Step 2: Customize Your Style and Theme
Tailor your course to reflect your brand and teaching preferences. Arlo offers a library of templates, themes, and multimedia assets. Choose the tone, style, and design that align with your objectives to craft a distinctive learning experience.
Step 3: Generate Quizzes with AI
Create quizzes that align with your course’s learning outcomes effortlessly. Arlo’s AI assistant pulls information directly from your course content, allowing you to generate effective quizzes in seconds.
Step 4: Design Interactive and Memorable Courses
Build courses learners will love by incorporating engaging multimedia elements. Use videos, infographics, and interactive activities to create an enjoyable and impactful learning experience. Arlo’s tools make it simple to craft content that leaves a lasting impression.
Step 5: Cater to All Learning Methods
Whether delivering microlearning, blended learning, or fully virtual sessions, Arlo has you covered. Use its features to create bite-sized modules, host virtual classroom sessions, or seamlessly integrate eLearning elements to meet any training objective.

Once you’ve created the course you can infuse it with interactive elements, including:
- Videos
- Slideshows
- Flashcards
- Hotspots
- Quizzes
- And much more.
Get Early Access to Arlo’s New Interactive Training Features
These examples should have given you some inspiration at how you can use different interactive elements to liven up the training you deliver.
The great thing about all of these interactive elements is that you can use them in conjunction with one another within a training program or course to create more dynamic and engaging learning experiences.
And the best part of all: you can incorporate nearly all of these interactive elements within your training with Arlo!
See Arlo for yourself
Schedule a personalized demo with our expert team and see how Arlo can automate all your training admin, so you can spend more time delivering great learning experiences.
Common Questions about Interactive Training:
1. What are the main benefits of using interactive training methods compared to traditional training?
Interactive training methods increase learner engagement, improve knowledge retention, develop practical skills by actively involving participants, and generally make for ‘funner’ training sessions. They offer a dynamic learning experience through techniques like scenario-based exercises, virtual reality simulations, and game-based learning, unlike passive traditional methods.
2. Can I use interactive training for topics like compliance and safety training?
Yes, interactive training is highly effective for compliance and safety training. Examples like VR simulations for emergency preparedness, scenario-based safety training, and interactive quizzes for identifying safety violations make it easier for learners to understand and apply critical safety protocols.
3. How can I create interactive eLearning content, and what tools are recommended?
You can create interactive eLearning content using various tools and techniques, including interactive videos, game-based learning, and interactive quizzes.
Platforms like Arlo, with its upcoming eLearning authoring features, allow you to design courses by converting documents, using AI to generate content, or building courses from scratch, with options to add multimedia and interactive elements.
4. Are self-paced courses considered interactive, and how can they benefit learners?
Yes, self-paced courses can be highly interactive, especially when designed with multimedia, quizzes, and other engaging elements. They benefit learners by offering flexibility, allowing them to learn at their own pace, and providing access to materials from various devices, making learning convenient and adaptable to individual schedules.
Interactive training can also help learners with critical thinking skills, communication skills and a range of other essential abilities, such as problem-solving, collaboration, and decision-making, by providing practical, engaging, and real-world scenarios.
5. How can I incorporate group collaboration exercises into my training programs, and what are some examples?
Group collaboration exercises can be incorporated through activities like “Bridge Build” and “Minefield,” which promote teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills. These exercises can be used in corporate training, workplace onboarding, and leadership development to enhance team dynamics, practical skills, and to test existing knowledge.
