Recently updated on March 17th, 2025
Instructor-led training remains a crucial training delivery method. From our customers at Arlo, we’ve heard that the demand for ILT has increased in the last couple of years.
Our own data, which shows the types of training or courses our customers are enrolling their learners in, also indicates an increase in the amount of instructor-led training being delivered, particularly face-to-face courses.
So in this article, we won’t be making any arguments about saying that ILT isn’t relevant anymore.
Rather, its about recognizing that some topics are better taught in a self-paced format, and many courses now blend delivery methods together, some modules are taught in person, some online, and some as eLearning modules.
And from our experience in talking with thousands of training providers one challenge ILT providers face is how to go about converting instructor led training into an eLearning format, and that’s why we’ve put together this guide.
We run through:
- A step-by-step process covering the key stages of converting ILT to eLearning
- How Arlo’s new and upcoming eLearning authoring tool can help you speed up the process of convert your existing training materials into engaging eLearning modules.
(Note: If you’d like to skip the reading and see how Arlo can help you create, schedule, deliver, and sell instructor-led training, blended courses, and eLearning, book a demo with our team.)
Converting Instructor-Led Training to eLearning Step-by-Step
Step 1: Adapt Existing or Define New Learning Objectives
The first step in the process involves assessing the learning objectives of the course you are looking to convert.
You may already have these in place if the course being converted is fully fleshed out, but if the ITL course is undergoing a significant restructure, you may need to come up with new learning objectives from scratch.
Adapting Existing Objectives
If you need to create new learning objectives, you can follow the tips we lay out below. If you’re just adapting existing learning objectives, keep these tips in mind for making them applicable to eLearning:
Focus on Outcomes, Not Replication
When adapting existing learning objectives, resist the urge to simply transfer content from the instructor-led format. Instead, analyze the core outcomes the original objective aimed to achieve.
Reframe the objective to emphasize measurable actions and demonstrable skills that can be assessed effectively in an e-learning environment.
For example, if you were converting a communications course, an existing learning objective might be “Understand the principles of effective communication.”
You could adapt it for e-learning as “Apply effective communication techniques in a series of simulated client interactions, demonstrating active listening, clear articulation, and empathy.”
This maintains the core objective while making it more action-oriented and suitable for an interactive e-learning environment.
Prioritize and Streamline Content
Instructor-led courses often have more time for in-depth coverage and tangential discussions. E-learning requires a more focused approach. Assess the existing learning objectives and identify the critical “need-to-know” information versus the “nice-to-know.”
Try and streamline the content to concentrate on the most essential elements that directly support the achievement of the objective. You can then organize the material into digestible modules that allow learners to master one concept before moving on to the next.
Instructor-led courses often have more time for in-depth coverage and tangential discussions. E-learning requires a more focused approach. Assess the existing learning objectives and identify the critical “need-to-know” information versus the “nice-to-know.”
Streamline the content to concentrate on the most essential elements that directly support the achievement of the objective. Organize the material into digestible modules that allow learners to master one concept before moving on to the next.
For example, in the same communications course, an original learning objective might be “Explain the 7 components of effective communication and their impact on various business scenarios.”
You could streamline this for e-learning as “Demonstrate proficiency in applying the 3 most critical components of effective communication (active listening, clear messaging, and non-verbal cues) in common workplace situations.”
This could be achieved in an e-learning course through:
- A brief introductory video explaining the 3 key components
- Interactive scenarios where learners practice each component individually
- A final assessment where learners analyze a workplace communication video and identify the effective use (or lack thereof) of all three components
Adapt for Interactivity and Engagement
Classroom environments naturally bring learners through discussions, group activities, and real-time Q&A.
eLearning needs to actively compensate for this by incorporating interactive elements that keep learners engaged and reinforce their understanding.
A good eLearning authoring tool should make this easy for you, the right tool will make it easy to add quizzes, drag and drop exercises, assessments, flashcards, videos, images, slideshows and more.
Defining New Objectives
If you need to come up with learning objectives from scratch, then you can follow these tips:
Determine the purpose of the training or course
Start by identifying what you aim to accomplish with the training program. If you’re working with a client you may need to conduct a training needs analysis to uncover any skills or knowledge gaps, which will guide the direction of your training.
Once you’ve done this you can start noting down the overall purpose of the course.
A couple of examples could be:
Conflict Resolution Training
Overall Purpose of the Training
To provide participants with the understanding and skills necessary to manage and resolve conflicts effectively in the workplace, promoting a more positive and productive work environment.
Time Management Course
Overall Purpose of the Course
To enable participants to optimize their time and improve productivity by teaching effective strategies for planning, prioritizing, and managing their workload.

Once you know the overall purpose you can start defining the broad, overarching eLearning course goals, addressing the “why” (e.g., improve effective communication skills in the workplace).
Then, break these goals into precise, measurable objectives, answering the “what” and “how”.
Measurable objectives provide the roadmap for both instructional designers and learners.
For example:
Goal: Improve effective communication skills in the workplace.
Objective: “By the end of this e-learning course, learners will be able to demonstrate the ability to apply effective communication techniques, including active listening, clear articulation, and empathy, in a variety of simulated workplace interactions presented through interactive modules.”
Define expected outcomes
Once objectives are defined, translate them into a clear, overarching expected outcome that is achievable in an online learning environment.
Be specific and use action verbs to describe what learners should achieve by the end of the eLearning course.
For example, given the objective: “By the end of this e-learning course, learners will be able to demonstrate the ability to apply effective communication techniques, including active listening, clear articulation, and empathy, in a variety of simulated workplace interactions presented through interactive modules,” the expected outcome might be:
Learners will successfully complete all interactive modules, demonstrating the consistent application of active listening, clear articulation, and empathy in simulated workplace interactions, and achieving an overall score of at least 80% on the integrated assessment activities.
Align eLearning objectives with business goals
If you’re designing an eLearning course for a client, make sure that the eLearning objectives tie back to broader business outcomes.
Consider how improved online learning experiences can contribute to organizational goals such as increased productivity, better customer satisfaction, or enhanced employee retention.
Apply the SMART format
Use the SMART format to refine your eLearning objectives. Make them Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
The SMART framework ensures that your eLearning goals are actionable and achievable within the digital learning environment.
Write from the learner’s perspective
Frame the objectives around what learners will be able to do or know by the end of the eLearning course. This can make the objective more engaging and learner-centric.
Use action verbs
Incorporate strong action verbs in your objectives to clearly describe what learners will do in the eLearning environment. For example, “demonstrate in an assessment”, or “analyze through interactive case studies”.
Keep it concise
Write objectives in simple, clear language. Avoid jargon or overly complex terms that might confuse online learners who don’t have immediate access to an instructor for clarification.
Prioritize objectives
Focus on the most important objectives that can be effectively achieved through eLearning. This will guide the learners’ attention to the skills that matter most and can be realistically developed in an online format.
Test your objectives
Finally, check that your eLearning objectives align with the company’s goals and that the online course is sufficient to meet those objectives. Ensure they are easy to understand and measurable through digital assessment methods.
Step Three: Auditing Your Existing ILT Content and Processes
Once you’ve come up with objectives, you can start auditing your current ILT content. Here are some tips on how to carry this out:
Is the content still relevant?
Is the current content still relevant and up-to-date? Has any of the information become obsolete or inaccurate? Are there any gaps in the content that need to be addressed?
Do the learning objectives still align?
Do the existing materials effectively support the defined learning objectives? Are there any discrepancies between the content and the desired outcomes?
How engaging and interactive is the content?
Identify elements that can be replicated or improved in an eLearning environment, such as group discussions, activities, or case studies. Also, pinpoint areas where engagement is lacking and consider how eLearning can offer improvements.
Delivery Methods
Analyze the effectiveness of different delivery methods used in the ILT setting. Determine which methods translate well to eLearning (e.g., presentations, demonstrations) and which might require adaptation (e.g., hands-on activities).
Assessment Strategies
Review the current assessment methods. Are they appropriate for measuring the learning outcomes? How can these assessments be adapted or improved for an eLearning format?
Existing Resources
Identify any existing resources that can be repurposed for eLearning, such as presentations, handouts, videos, or other multimedia materials. This can save time and effort in the conversion process.
Learner Feedback
Gather feedback from past participants on their experience with the ILT. What did they find most helpful? What areas could be improved? Learner input can inform the design of the eLearning modules.
Step Four: Redesigning the Instructional Design Strategy to Suit eLearning
Building upon the foundation of well-defined learning objectives and a thorough audit of existing ILT materials, the next step is redesigning the instructional design strategy to fully leverage the capabilities of eLearning.
This involves a shift in mindset from a primarily instructor-led approach to a learner-centered, self-paced, and often asynchronous learning experience.
Here’s some tips on how you can translate the previously established objectives and audit findings into an effective eLearning instructional design:
Map Objectives to eLearning Activities
For each learning objective, determine the most effective eLearning activities to achieve it.
Consider:
Knowledge Acquisition: For objectives focused on knowledge recall or understanding, eLearning can utilize interactive readings, videos, infographics, and quizzes.
Skill Development: Objectives requiring skill demonstration can be addressed through simulations, interactive exercises, virtual labs, and branching scenarios.
Application of Knowledge: Case studies, problem-based learning activities, and real-world simulations allow learners to apply their knowledge in realistic contexts
Structure Content for Online Delivery: : Break down large chunks of content into smaller, manageable modules. This facilitates microlearning and allows learners to progress at their own pace.
If this process seems somewhat overwhelming it is an option to seek out the services of an experienced instructional designer who can guide you through each step
You can check out Arlo’s learning design services for help with this.
Step Five: Choosing an Appropriate eLearning Authoring Tool
By now you’ll have examined and identified the learning objectives for the ILT course you’re looking to convert, you’ll have audited your current content and processes and begun mapping out ways to start transitioning elements of your ILT course to an appropriate eLearning equivalent.
Now that the prep work is out of the way the more exciting part of the process can begin – choosing an eLearning authoring tool to start creating your eLearning!
(Note: You can get some insights into some of the different eLearning authoring tools available in our article: 13 Best eLearning Authoring Tools, Platforms and Software for 2025)
Some high level factors to keep in mind when you’re choosing an authoring tool are:
Content Creation Speed & Scalability: How many courses will you offer, and how often will they need updating? Choose a tool that enables rapid development and easy updates to respond quickly to changes. AI-powered tools can further accelerate this process.
Branding & Customization: Can the tool style courses match your brand (colors, fonts, logo) or those of your clients? This is crucial for maintaining brand consistency.
Budget & ROI: While budget is important, consider the potential return on investment. eLearning expands your reach, creates new revenue streams (online learning is a booming market), and can significantly boost productivity (studies suggest up to 30% gains).
It also improves client satisfaction by offering tailored training and flexible delivery methods.

Step Six: Producing Your eLearning Course With the Authoring Tool
For this step, we’ll walk you through the key features of Arlo’s upcoming eLearning authoring features, and you may find that it’s the exact tool you need to convert your ILT content into engaging, eLearning content.
With Arlo, you’ll soon have the tools to create and design engaging eLearning content.
Here are the three ways you’ll be able to do this (and step by step instructions):
- Document to Course – Upload and convert existing documents into interactive courses.
- Generate a Course with AI – Enter a description of your course into Arlo’s AI assistant, select your tone, style, fonts, colors, and branding, and watch as your course is created before your eyes.
- Build Your Course from Scratch – Use Arlo’s course and quiz templates to create your course from the ground up.
1. Document to Course
The document to course option allows you to convert your existing ILT materials into eLearning content.
Step 1: Prepare Your Document
Arlo supports various file formats, including Word documents, PowerPoint presentations, and PDFs. If your content is stored on an external platform, export it as a PDF to get started.
Step 2: Upload Your Document and Choose a Course Style
Upload your file to Arlo and select a course style that aligns with your objectives. Whether you prefer a concise layout, a focus on key information, or a more creative design, you can customize the tone and appearance to suit your needs.
Step 3: Transform Your Document into an Interactive Course
Let Arlo do the heavy lifting as it converts your document into a fully interactive eLearning course. Once the transformation is complete, review the content, adjust layouts, add multimedia, or further customize the course to meet your vision.
2. Generate a Course with AI
The second way of creating an eLearning course involves inputting your description into Arlo’s AI eLearning assistant. You’ll then be prompted to choose the style and tone of your course, and a full course outline will be generated, ready for you to customize.

Step 1: Provide Input to Arlo’s AI Assistant
Share the details of what you want your course to cover with Arlo’s AI assistant. The more specific and detailed your input, the more tailored and relevant your course will be.
Step 2: Choose Your Style, Tone, and Theme
Select from a variety of styles, tones, and themes to customize your course. Finish it off by applying one of Arlo’s professionally designed course templates to create a polished, cohesive look.
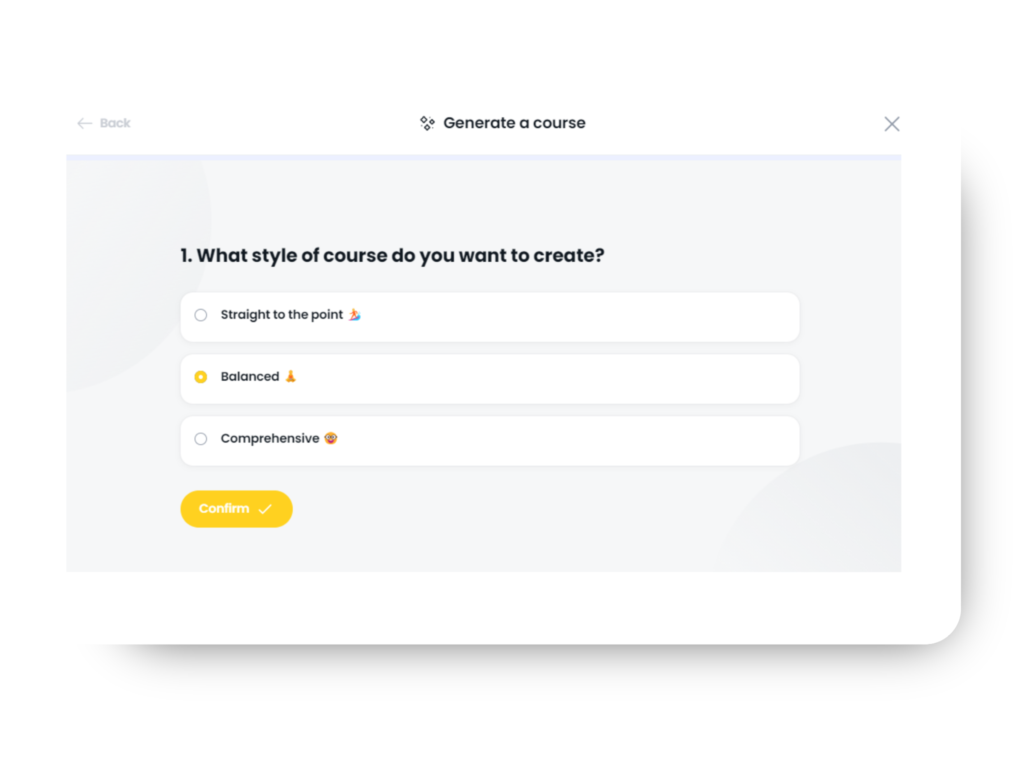
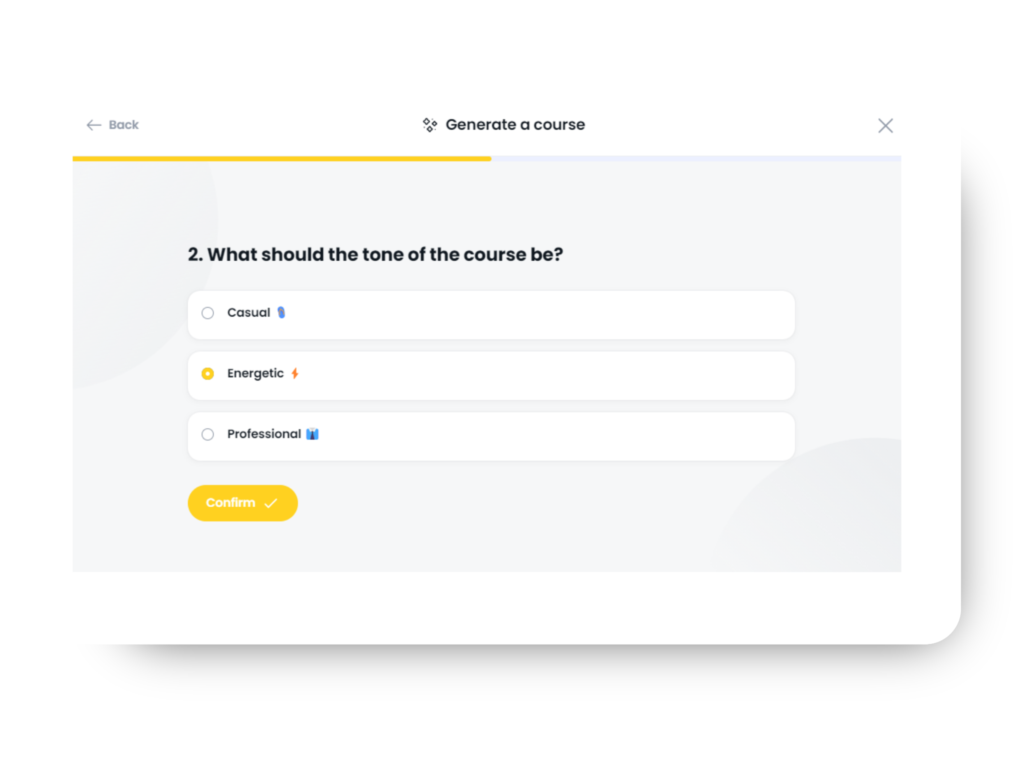
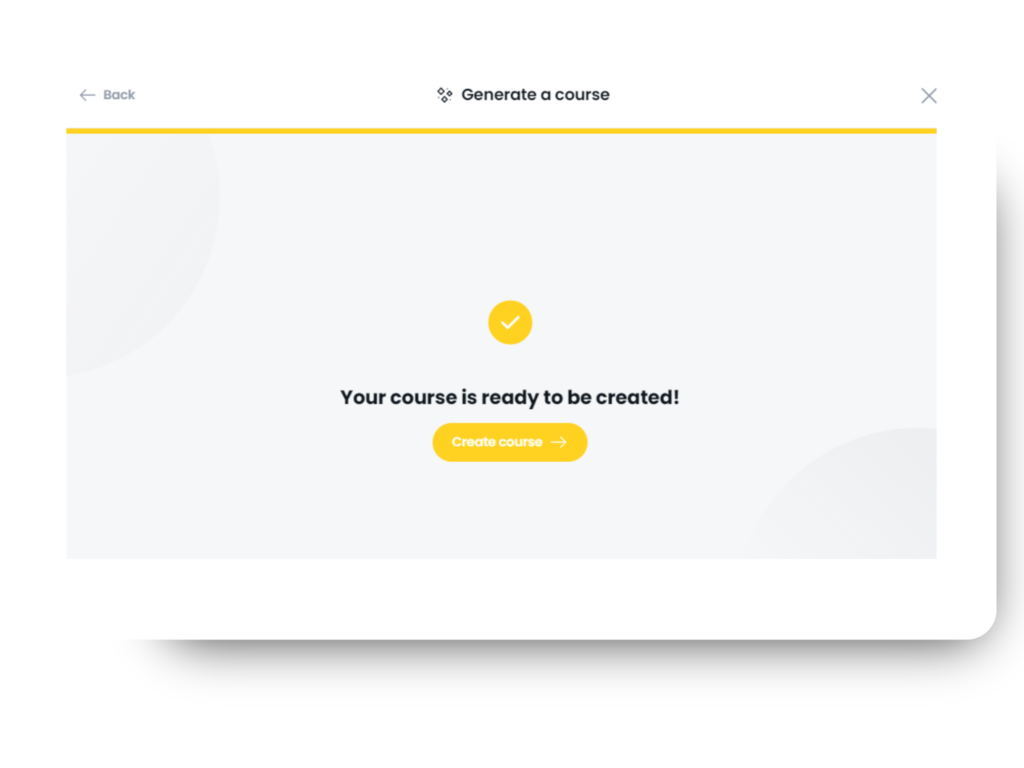
Step 3: Watch Your Course Come to Life
Arlo will build your course section by section based on your input. As the content comes together, you can review it, make edits, and refine it to ensure it aligns perfectly with your goals.

3. Build Your Course from Scratch
The third option involves you have full creative control over the course creation process.
Step 1: Design and Structure Your Course
Begin by outlining your course using Arlo’s intuitive interface. Organize your content into sections or modules, and add multimedia elements such as videos, downloadable resources, and interactive activities to create a solid foundation.
Step 2: Customize Your Style and Theme
Tailor the appearance of your course to align with your brand and teaching style. Select from a range of templates and themes to create a cohesive, professional look. Adjust colors, fonts, and layouts to reflect your objectives.
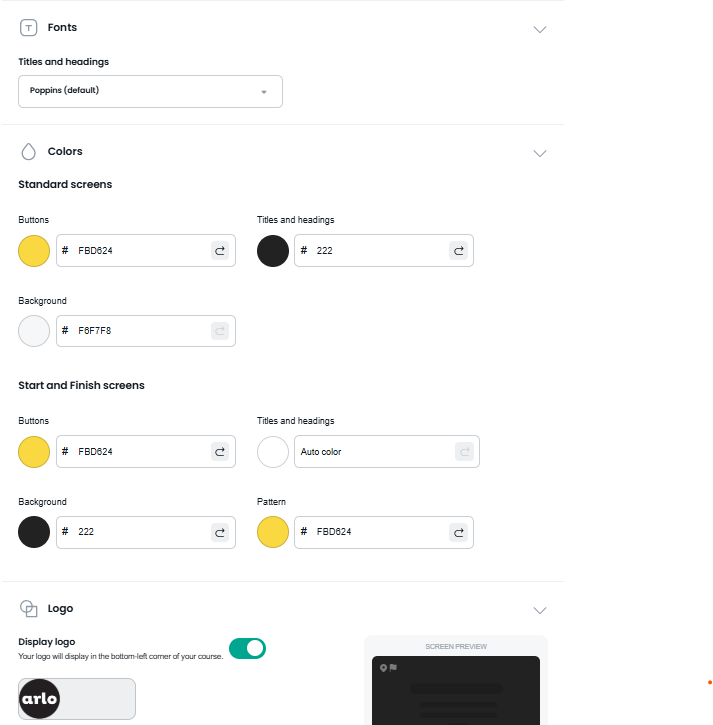
Step 3: Add Assessments and Quizzes
Include quizzes and assessments to reinforce key concepts and measure progress.
Arlo’s AI assistant can generate quiz questions directly from your course content, helping you save time and ensure alignment with your learning goals.
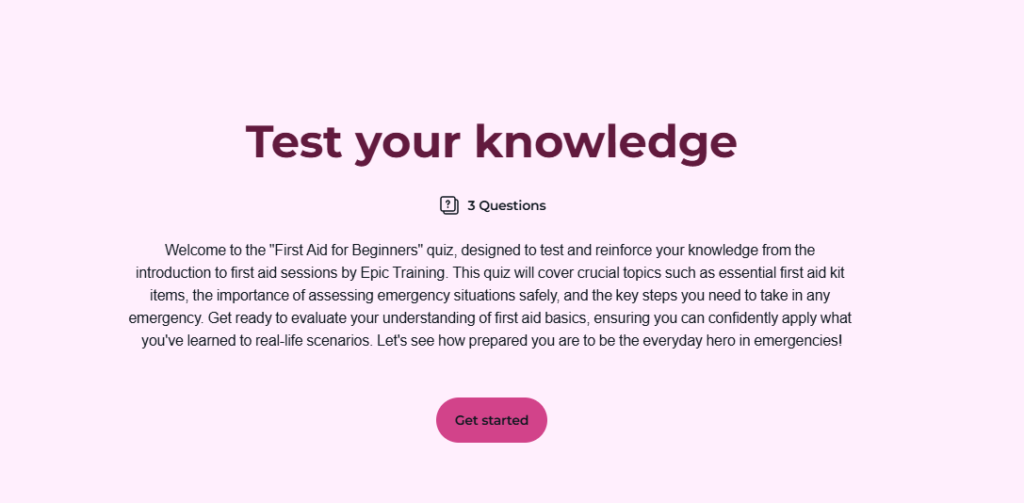
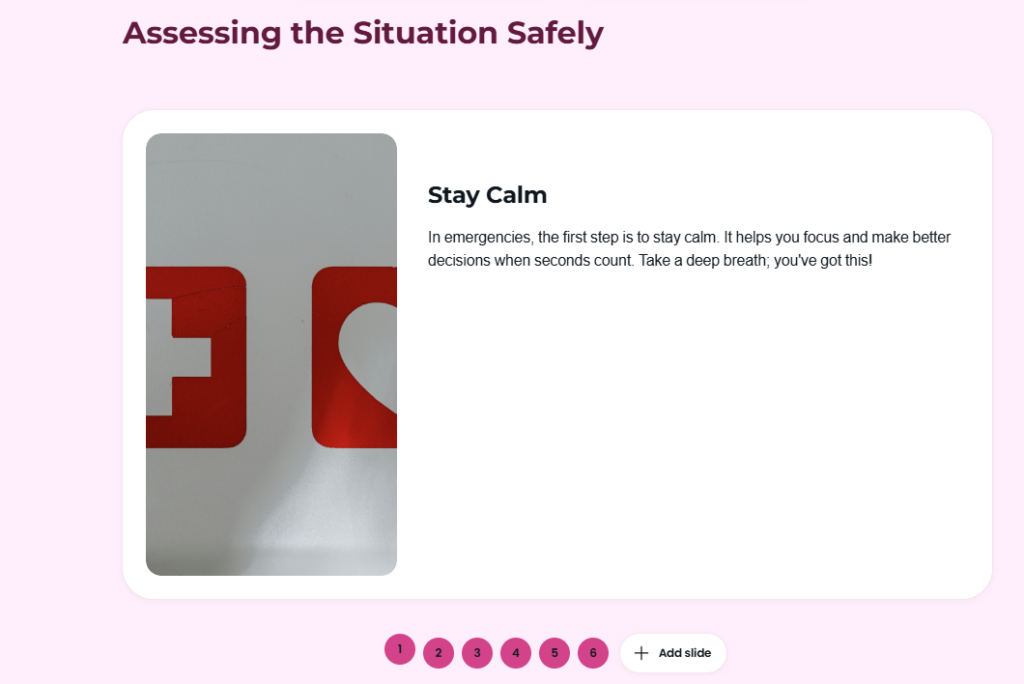
Step 4: Enhance Engagement with Interactive Features
Incorporate interactive elements like flashcards, infographics, gamified challenges, and practical activities. These features keep learners engaged and help them retain knowledge more effectively. Arlo’s tools make it easy to create a dynamic and impactful learning experience.
Whichever option you choose your eLearning course will be ready in minutes, ready for you to add further content to, edit and customize.
Step Seven: Adding Visual and Interactive Elements to Your eLearning Content
You may have completed this step when creating your eLearning course, but if not, it’s time to ensure you’ve added interactive elements. If possible, as mentioned earlier, map the interactive elements you wish to include to your learning objectives.

For example, if participants need to complete an assessment or quiz to successfully achieve a learning objective or outcome, the eLearning authoring tool you use must have the necessary features to incorporate these elements.
Other key interactive elements that you can add to your course with the right authoring tool are:
- Images
- Videos
- Slideshows
- Accordions
- Step by Step Instructions
- Flashcards
- Checklists
- Gamification Elements
- Simulations
- Infographics
- Audio Clips
- Drag-and-Drop Activities
- Scenario-Based Learning
- Discussion Forums/Chats
- Polls/Surveys
- Virtual Reality (VR) or Augmented Reality (AR) Experiences
- Interactive Diagrams or Flowcharts

Step Eight: Testing Your eLearning Modules
When you’re happy with your course, and you’ve added all your interactive elements, the final step before launch is to test it to make sure all of the functional aspects are working correctly.
You’ll also want to make sure you’re happy with all of your content, make sure there are no spelling or grammar errors, etc. If you have the capability, it is also a good idea to take your course for a test run by a colleague or fellow subject matter expert.
Another possibility is to take the course for a pilot test with a small number of participants. Doing this can help you iron out any potential issues.
Within Arlo’s eLearning authoring tool, you can preview what your course will look like on desktop, tablet, and mobile before launching.
After you’re happy with how it looks, you can also share a link to the course easily before it’s published if you want someone else to review before it goes live.

Step Nine: Launching Your eLearning Course
Once tested you’ll be ready to launch your eLearning course. How you do this will be dependent on the platform you are using, if you create your course through an LMS you can set it live within the platform.
If you use a standalone authoring tool it should allow you to share the course to your LMS.
If you’re using Arlo, you can schedule your eLearning course to your website or internal portal, either as a standalone course or as part of a blended learning program.
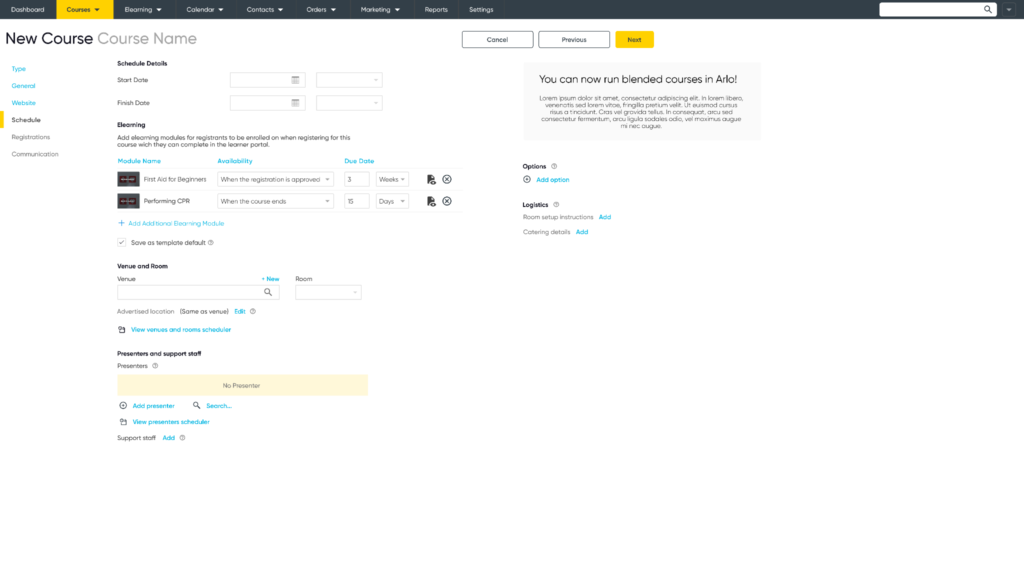
Step Ten: Evaluating and Reporting on Your eLearning Modules
There are numerous metrics you can use to report and evaluate your eLearning course. Most LMS platforms and authoring tools enable you to track key metrics such as course completion rates, participant engagement, test scores, time spent on each module, learner feedback and more.
Some platforms also integrate with tools such as SurveyMonkey to help you gauge more qualitative feedback from learners. Arlo, for example,allows you to create pre and post-training surveys through its integration with SurveyMonkey.
After connecting your Arlo account to SurveyMonkey, you can set up surveys either within Arlo or SurveyMonkey and schedule them to send at the desired time.
Our customers use these surveys to capture feedback on all kinds of important topics related to the training they offer. Surveys are fully customizable to the questions you want to ask and feedback you want to receive.
Related Read: 29 Training Survey Questions Ideas to Kickstart Your Learner Feedback Process
If you’re looking to get more granular with specific metrics, you can do so through Arlo, particularly if you want to drill into the financial performance of the courses you run. You can generate various reports, including:
- Registration Reports: Track attendance rates, course participation by organization, trends over time, and course completion rates.
- Order Reports: Analyze financial performance, such as revenue generated per course, earnings per course, and much more.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
You should now have an idea of a process you can follow to convert an instructor-led training course to an interactive, engaging eLearning variation.
Of course, this process can be adapted, the aim was to give you an understanding of the key points to consider, and show you how Arlo’s new eLearning features can help make the process quicker and easier!
If you’d like to sign up for early access to these new features, and kick-start your ILT conversion process, simply click the link below and fill out the early access form! 👇
Want to be first in line to try Arlo’s new eLearning authoring features? Sign up for early access!
We’ll be in touch with details for early access as we get closer to launch. You’ll be contacted first!